Smart Traffic System
Since developing the intelligent transportation system, the demands to the system have already exceeded the system can provide. Therefore, these smart traffic applications have been integrated into the smart city's vehicle network developing strategies in order to create an interactive, interconnected, and convenient living society. The mobile capabilities of the system are enhanced as well while technologies advancing.
1.Automated Vehicle Location System
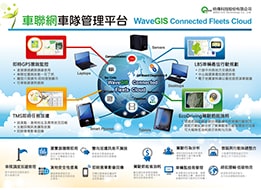
Through GPS coordinates by satellite tracking and positioning, integrating vehicle anti-theft, off-road tracking, driver’s driving statuses, front-to-rear collision avoidance and warning, logistics cargo tracking system as well as vehicle CAN (Controller Area Network) bus information, this fleet management system features, applications and functionalities fully exert in different industries and become the core management information for enterprise operations. It is also a role model for applications in smart transportation techniques
2.Vehicle Network Telematics Architecture & Applications
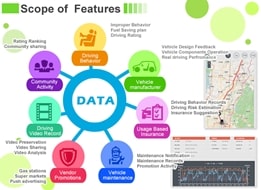
The application combines the infotainment, safety, navigation and social networking for driving and sharing. It creates the possibilities of Big Data for regulating car insurance policies, optimized vehicle maintenance and enriched driving experiences. Applying Telematics to develop Internet of Vehicles (IoV) architecture and applications. The system successfully addresses vehicle network interconnecting demands, provides technical services in the areas of logistics management, smart automotive navigation, parking lot management and traffic flow. In addition, the system can enter into automobile markets by providing customers’ personalized auto-services, for example, involving vehicle activities or movement, car insurance and other related applications.
Intelligent Flood Defense
Applying Internet of Things technology, including sensing components and big data platform, the architecture can assist organizations to establish a water-related disaster monitoring system, develop and deploy flood warning capabilities as well as cloud computing and modeling simulations. Furthermore, the system can integrate and coordinate with forecasting mechanisms and aggregate measurements in real time to provide timely assistance in water disaster prevention or mitigation analyses as well as decision support makings.
1.Intelligent Flood Defense Project in Tainan City
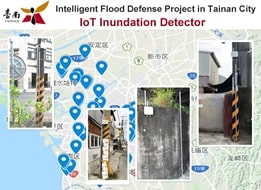
Installed 55 IoT based water level sensors to detect urban flash floods. The project can transmit water level data via LPWAN network (including LoRa and NB-IoT modules) and perform inundation impacts assessment in real-time.
Other Similar Clients:2nd,3rd, 5th and 10th River Office,Chiayi County,Hsinchu City, New Taipei City.
2.Mobile Pumping Machinery Tracking & Management System in Chiayi County
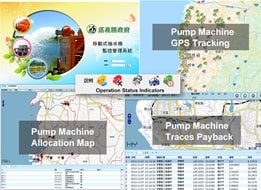
The System tracks and manages mobile pumping machinery in the county drainage regions. It has developed and deployed by tracking the machines’ locations and their operational statuses in order to allocate and dispatch the machinery coverage or distribution over the regions effectively and efficiently, especially during hazardous occurrences.
Other Similar Clients:Water Resource Agency,Ministry of Economic Affairs
Yilan County, New Taipei City, Changhua County.
3.Local Area Flood Warning System

The System integrates Geo Data, such as rivers, drainages, digital elevation model (DEM) and other demographic, economic, or land usage datasets including potential inundation maps and real-time water level sensing data, rainfall, streaming videos along the rivers and drainages to provide floods early warnings and analyze associated impacts.
Other Similar Clients: Keelung City,Yilan County, Chiayi County,Hsinchu City, Changhua County.
Smart River
Smart Rivers project has been aiming to manage rivers and riverside landscapes. It expects to reduce flood severity and flood damage; people and communities, in the river basin neighborhoods, are resilient to river floods. In addition, the project evaluates and reinforces the capabilities of transmitting hydrological measurements or observations based upon real practices and experiences over dynamic variations of river basins. By adapting IoT technologies, implementing hydrological or hydraulic functionalities as well as attaining missions of River Management Offices, Smart Rivers project has been subjected to install: (1) flood sensors to measure inner/outer water levels of gateways in water pumping stations; (2) vibration sensors to estimate or evaluate the safety of levees along rivers; (3) wireless tracer for streambed scouring detection and stabilities of bridges. All these IoT based sensing data can provide floods prevention and disaster mitigation information for River Management Offices, Water Resources Agency, Taiwan.
The Smart Rivers project applies the technologies of Internet of Things to enhance intelligent approaches on river management, hydrological data monitoring, flood warning and forecasting capabilities, as well as flood prevention, control or mitigation. By linking rivers, districts and regional sensing facilities, involving interconnected low-power transmitters to aggregate the existing sensors’ measurements including water level, flow rate, water levels inside and outside a gateway of a water pumping station, operating or accessing other engineering variables, as well as flooding sensing facilities, the Smart Rivers project can achieve hydrological or hydraulic parameters monitoring, investigating and evaluation. The project establishes a flood control early warning and response management system. The objectives of the platform can be further explored and developed to analyze and deploy artificial intelligence strategies on water related activities to cost-effectively handle water resources and decision support makings.
1.Smart river applicaitions and evaluation for Tamsui River
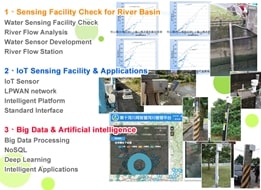
IoT based water level sensors were installed in the Tamsui river basin for flood detection and prevention. The project transmits water level data via a NB-IoT module. The data transfer intervals are pre-configured according to the inundation depths in order to save power consumption of the devices. The higher the inundation depth is measured in the river basin, the shorter the data transmit interval is configured.
This project is a pilot run for a simple and low cost water level monitoring station which combines barometric pressure water level sensor embedded with a NB-IoT transmission module. After the run, it indicates that this water monitoring station can operate reliably and cost-effectively. The experiment also concludes that the possibility of additional water stations can be installed over river basin.
2.Smart river management in Touqian River.
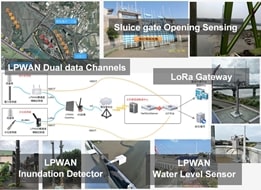
Taking Touqian River as a target, applying Internet of Things to:
(1) integrate real-time monitoring instruments;
(2) aggregate monitored engineering parameters;
(3) execute simulation forecasting models, disaster statistics models, inundation simulation model;
(4) automate value-added analysis modules;
(5) present flooding images or CCTV outputs on GIS display platforms over interested areas or locations.
For example, engineering parameters or statuses of sensors or devices include measuring flood depths via water level sensors; allocating relevant locations and installing multiple water pumping stations (including internal and external water level gauges along a pumping station pathway), obtaining CCTV images, handling sluice gate opening and operating statuses, calculating flow velocities and volumes, detecting inclines of river banks, etc. The aggregated data are transmitted via LPWAN to the back-end servers or Azure Cloud for further feature analyses and/or modeling simulations.
In summary, this IoT Smart Rivers Management System is established based upon elements and facilities to automatically and quickly generate sensing information in real-time those are needed for disaster forecasts and preventions. It can improve dramatically on effectiveness and efficiency of disaster estimations and predictions. It can instantly grasp physical engineering measurements and reduce modeling execution and evaluation time. In other words, the System creates early warning alerts and increases evacuation periods when disasters occur unexpectedly.
Other Similar Clients: 3rd ,5th and 9th River Office, Water Resources Agency (WRA), Taiwan.
Smart Environmental Monitoring
Implementing IoT technologies, a smart environmental monitoring application has created an open standard and great opportunities for low-cost, sime-automated real-time, remote environmental monitoring system to measure physical entities, such as air quality, traffic flow, water resources usages or city safety issues.
1.Remote sabo dam monitoring & auto-assessment for Soil & Water Conservation Bureau
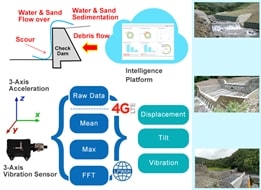
By applying 3-axis vibration sensors, the system can detect and analyze vibration patterns autonomously, and it issues alerts and transmits them, via LPWAN networking, while the measurements exceeding their thresholds. In other words, the system can monitor, control and sustain the long –term stabilities of numerous sabo dams, levees, flood prevention walls, dikes or weirs cost-effectively.
Applying intelligent, low cost, standardized technologies of Internet of Things, a platform integrates with vibration sensors can monitor, measure and obtain engineering parameters, such as dam structural displacement, vibration, incline, etc. Moreover, it can perform relevant features’ computing and calculation. When the parameter value exceeds threshold(s), the platform will issue warning(s) and transmit alert(s).
By implementing innovative monitoring and communication technologies to establish a smart information platform. The platform can promote the scale of sediment transportation monitoring facilities and achieve goals to inspect, control and manage sabo dams.
In summary, vibration sensors can monitor, aggregate, analyze, and detect dam vibration patterns autonomously. The platform transmits alerts when the measurements reach thresholds via LoRa network. To reduce the power consumption of a sensor, the sensor encloses a built-in Lithium-ion battery.
2.A Smart IoT Integrated Reclaimed Water Treatment Platform in Shui-Nan Economic and Trade Park, Taichung City
The Taichung Municipal Government has been taking the lead in stimulating and implementing wastewater or sewage treatment programs in the Shui-Nan Economic and Trade Park. The Shui-Nan Water Recycling Center has the largest scale of Membrane Bioreactors for Municipal Wastewater Treatment System in Taiwan. This water reclamation system converts domestic wastewater into reusable water. According to the estimation of the Water Reclamation Organization, it indicated that this recycling center can reduce approximately 52,500,000 tons of running water usage and save NTD 50M water bill annually in the community.
The Shui-Nan Water Recycling System integrates Smart IoT technologies into the wastewater treatment applications. The target of the project is to intelligently monitor, aggregate, convert and recycle wastewater or sewage into an effluent to be reused in this community. For example, after the domestic wastewater is properly being treated by the System, the effluent or reclaimed water can be reused for irrigating gardens or agriculture fields, flushing toilets, washing vehicle or other residences, business or industry usages. It not only increases the flexibility of water resources, but also effectively alleviates water shortages in the regions.
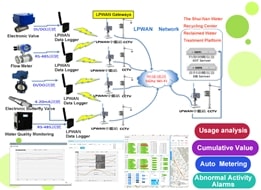
The Water Recycling Center can convert 18,000 tons of domestic wastewater into reusable water daily. The water reclamation system integrates Smart Internet of Things (IoT) related techniques and methodologies. It can instantly monitor and aggregate various physical measurements, for example, water quality, pressure, flow velocity, and flow regulation via operating butterfly valve, valve control, as well as other engineering parameters. The system can transmit the physical measurements under real-time to a centralized intelligent information management platform or Data Center in order to carry out water resources operations. Apparently, the platform can dynamically control, manipulate, and manage reclaimed water supply/dispatch activities as well as obtain statuses of sensors or devices in the regions in order to respond accordingly and correspondingly under real time.
The water reclamation system adopts LoRaWAN communication mechanism between the data logger gateway and the Data Center. The data logger aggregates and transmits the monitored engineering parameters, as listed above. It can transmit 16,000 measurements every 10-min interval approximately. The CCTV images are transited to the Data Center directly, not collected by the data logger. In addition to monitoring the engineering measurements, the Water Recycling System provides (1) users’ authentication/authorization verification and validation processes; (2) historical records of engineering parameters, i.e., water level, water quality values, and (3) trigger alarm capabilities while the threshold settings are exceeded. This centralized, intelligent platform can improve, enhance and promote Big Data Analyses for the Park as well.